52
number of oil and gas extraction facilities in Poland (2020: 53)
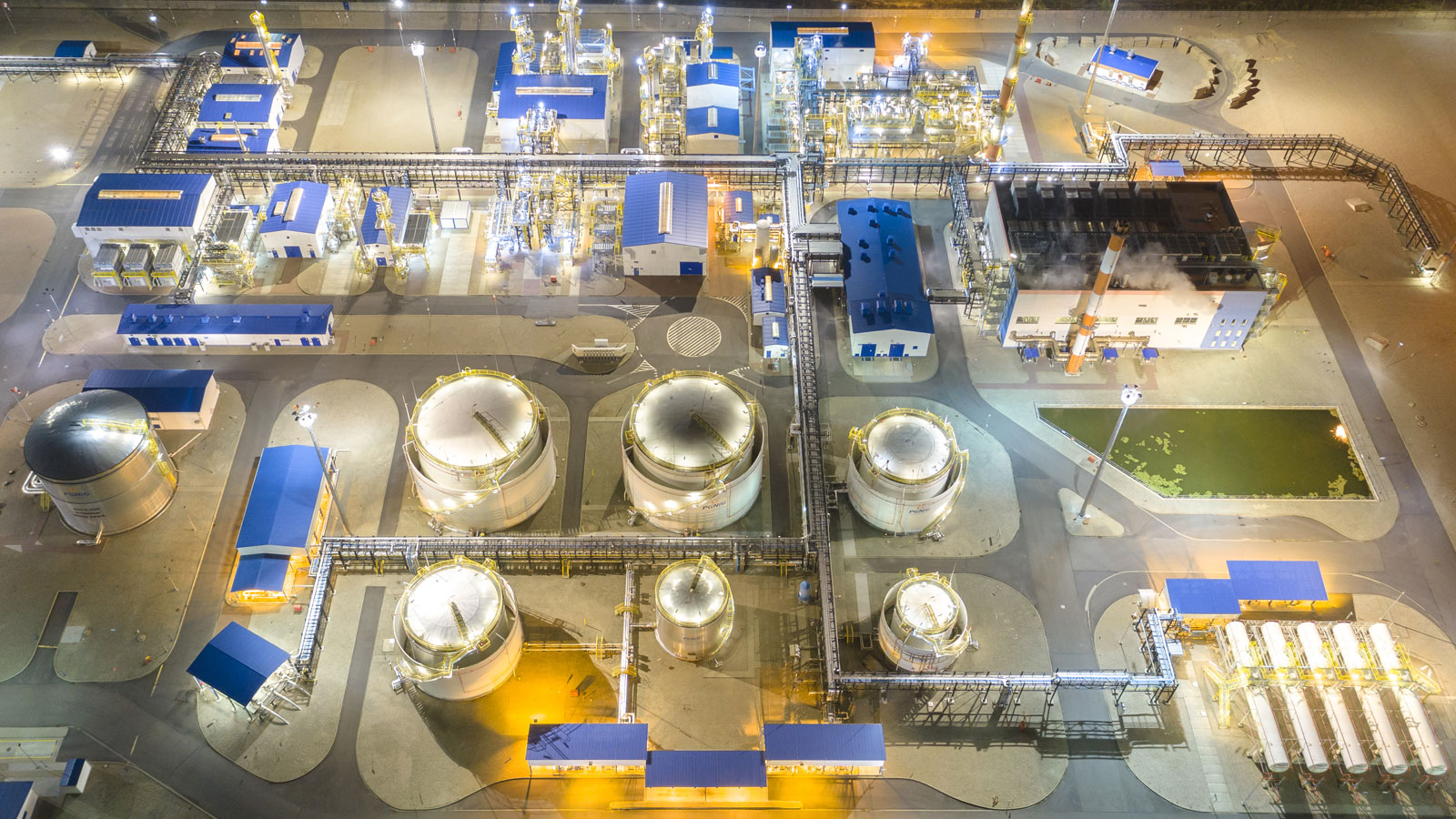

We define manufacturing capital as the property, plant and equipment used by the PGNiG Group to conduct its business. The key items of the Group’s property, plant and equipment are buildings and structures and plant and equipment, mainly that associated with exploration for and production of natural gas and crude oil and with gas trading, storage and distribution.
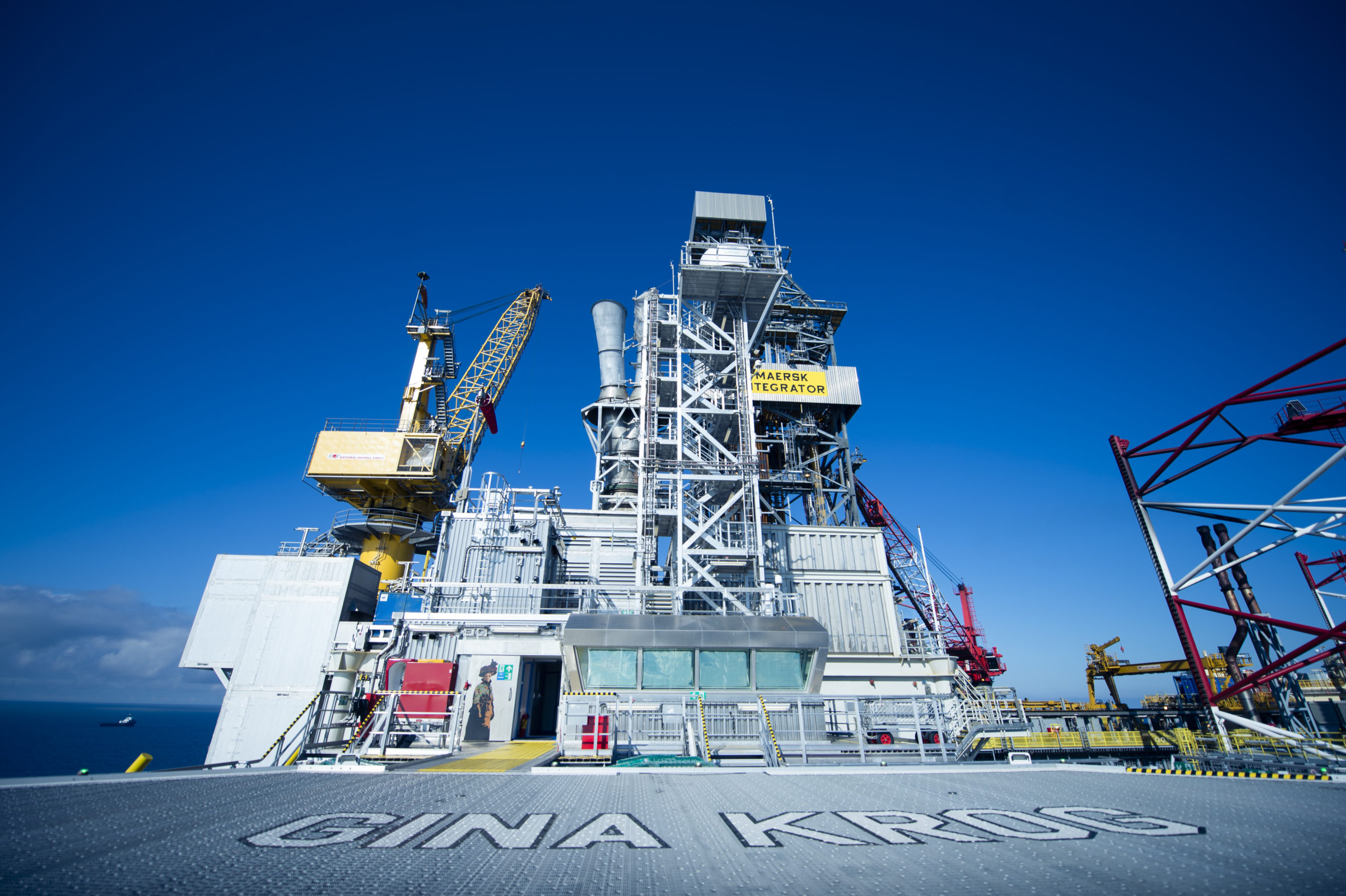

52
number of oil and gas extraction facilities in Poland (2020: 53)
188
number of production licences in Poland (2020: 189)
>2,000
number of production wells (2020: over 2,000)
47
number of licences for exploration for and appraisal of mineral deposits in Poland (2020: 47)
58
number of licences on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (2020: 32)
3
number of countries in which the Company has production operations (2020: 3)
2
number of L group gas storage facilities (Daszewo and Bonikowo underground gas storage facilities) with a total capacity of 0.26 bcm (2020: 0.26 bcm)
7 – underground gas storage facilities, located in Brzeźnica, Husów, Mogilno, Strachocina, Swarzów, Wierzchowice and Kosakowo, with a total capacity of 3.2 bcm (2020: 3.2 bcm)


201,000 km
length of PGNiG Group’s own network, including service lines (2020: 195,000 km)
1,697
number of municipalities connected to the gas network (2020: 1,666)


18
generating units (2020: 17)
6.0 GW
thermal power (2020: 5.2 GW)
1.8 GW
electric power (2020: 1.2 GW)
70%
estimated percentage of heat demand in the Warsaw market covered by the PGNiG TERMIKA Group
65%
estimated percentage of electricity demand in the Warsaw market covered by the PGNiG TERMIKA Group
1.4
m tonnes crude oil and NGL production (2020: 1.3m tonnes)
5.4
bcm natural gas production (2020: 4.5 bcm)
33.5
bcm natural gas sales by volume (2020: 30.7 bcm)
5.4
bcm natural gas imports by volume (2020: 14.8 bcm)
* including transactions on the Polish Power Exchange
13.1
bcm distributed gas by volume (2020: 11.6 bcm)
19.3
bcm estimated volume of gas fuel transmitted over the network, according to GAZ System (2020: 18.1 bcm)
7.4
m number of customers (2020: 7.3m)
41.2
PJ heat output (2020: 38.4 PJ)
3.5
TWh electricity output (2020: 3.6 TWh)
PLN 2,108m – capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment in 2021 (2020: PLN 2,557m)
PLN 1,295m – capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment abroad in 2021 (2020: PLN 1,707m)
PLN 80m – capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment in 2021 (2020: PLN 90m)
Construction of Cluster B continued at the Kosakowo CUGSF with a view to obtaining additional working capacities
PLN 3,227m – capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment in 2021, including spending on gas network expansion and upgrade projects (2020: PLN 2,945m)
PLN 2,135m – capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment in 2021, including PLN 582m of CO₂-related spending (2020: PLN 1,076m, including PLN 500m on CO₂)
Construction of a ca. 450 MW CCGT unit at the Żerań CHP plant (Żerań CCGT)
Letter of Intent signed with PKN Orlen on cooperation in the construction of a gas-fired generating unit at the Ostrołęka CCGT plant
Upgrade of the Pruszków CHP plant
Construction of a solar PV plant at the Kawęczyn heat plant
Investments related to adapting generation plant and equipment to BAT (Best Available Techniques) requirements
Data as at December 31st 2021
One of the key directions for Group-wide innovation efforts is to improve the efficiency of production assets managed by the individual companies. Innovators and startups are contributing to the fast growth of the PGNiG Group by inspiring innovation projects fitting into global trends, which could not be realised without access to the PGNiG Group’s assets enabling experts to perform tests and pilot implementations in the production environment. As a result, technology development, which is to be ultimately commercialised, progresses much faster.
The PGNiG Group strives to build a culture of employee engagement and drive innovation. In the case of energy companies, the problem of generation gap is becoming increasingly widespread. Despite advancing automation, the efficiency of production assets remains hugely dependent on the availability of qualified technical personnel.
PGNiG takes measures to recruit highly qualified staff and manage the generational shift through projects such as:
Interactions between natural capital and manufacturing capital may be analysed on several levels.
Property, plant and equipment are the largest component of the PGNiG Group’s assets. As at December 31st 2021, their value reached PLN 50,192m. Investments in production assets require the use of external funding raised in the financial market or internal funds held by the Group. In line with the PGNiG Group Strategy ratified in March 2017, the capital expenditure guidance for 2017−2022 has been set at over PLN 34bn. Average annual capital expenditure in 2017−2022 will amount to ca. PLN 5.7bn:
Renewable energy sources are a new strategic area for the PGNiG Group, with around PLN 4bn allocated to building the renewable energy segment.
In 2021, the PGNiG Group’s capital expenditure on property, plant and equipment was approximately PLN 7.7bn, having gone up by 13% year on year.
In addition to expenditure on new production assets, the maintenance and upgrades of existing plant and equipment is also a major component of CAPEX. In 2021, Polska Spółka Gazownictwa alone spent some PLN 2.18bn to roll out the gas network and connect new customers, and around PLN 0.84bn to alter and upgrade the gas network. The Generation segment bears significant costs of adapting its generation plant and equipment to BAT requirements.
In the mid- and long-term perspective, the goal of investments in the asset base is to enhance the Group’s efficiency and upscale its business. In line with the stated strategy of the PGNiG Group for 2017–2022 with an outlook until 2026, the CAPEX programme is expected to deliver cumulative 2017–2022 EBITDA of approximately PLN 33.7bn, driving long-term growth of the Group’s EBITDA in 2023–2026 to the annual average of around PLN 9.2bn.
The Group’s operations and the location of its production assets have a direct bearing on the living conditions and development of entrepreneurship across all regions of Poland.
By engaging in the anti-smog campaign, the PGNiG Group promotes natural gas as a source of energy. The green products and services offered by the PGNiG Group to its customers included: